Data Pipeline Architecture Explained: 6 Diagrams and Best Practices
In this post, we will help you quickly level up your overall knowledge of data pipeline architecture by reviewing:
Table of Contents
Be sure to read to the end where we share 6 data pipeline architecture diagrams used by real data teams at companies like JetBlue, Fox Networks, Drata, and more. Let’s go!
What is data pipeline architecture?
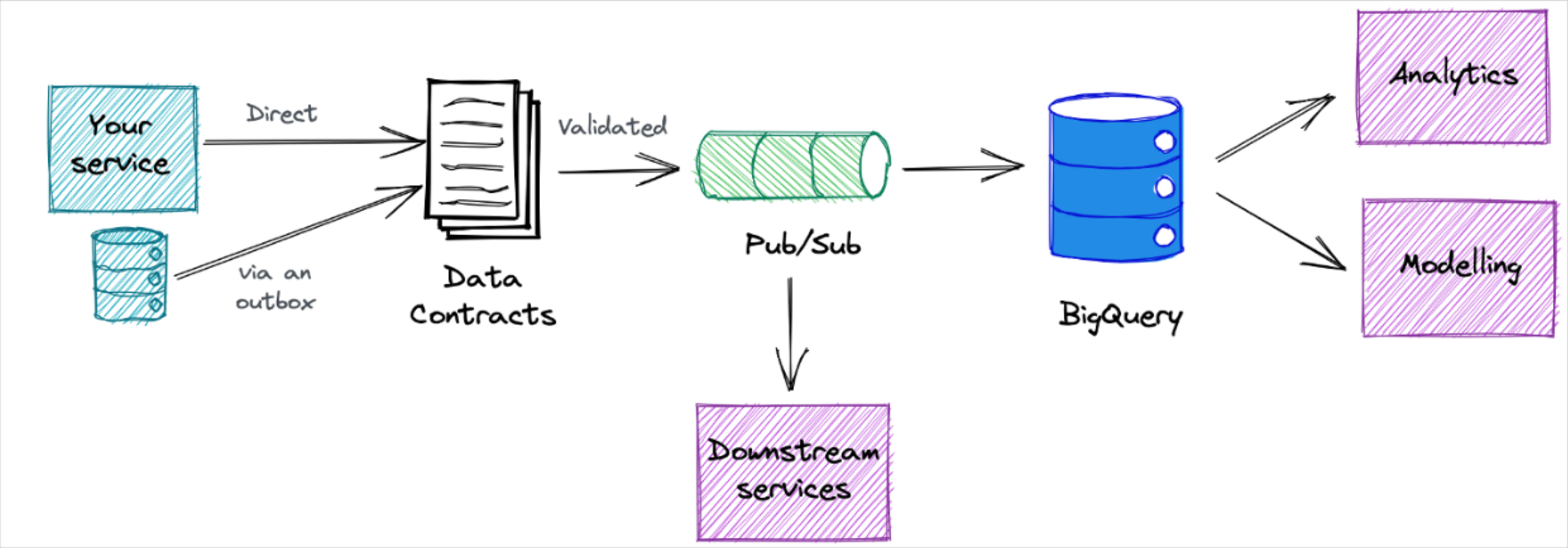
Data pipeline architecture is the process of designing how data is surfaced from its source system to the consumption layer.
This frequently involves, in some order, extraction (from a source system), transformation (where data is combined with other data and put into the desired format), and loading (into storage where it can be accessed). This is commonly abbreviated and referred to as an ETL or ELT pipeline.
It’s important to understand most data pipelines aren’t a linear movement of data from source A to target B, but rather consist of a series of highly complex and interdependent processes. For example, data may be extracted from multiple sources, reorganized, and joined at different times before ultimately being served to its final destination.
Why is data pipeline architecture important?
For data engineers, good data pipeline architecture is critical to solving the 5 v’s posed by big data: volume, velocity, veracity, variety, and value. A well designed pipeline will meet use case requirements while being efficient from a maintenance and cost perspective.
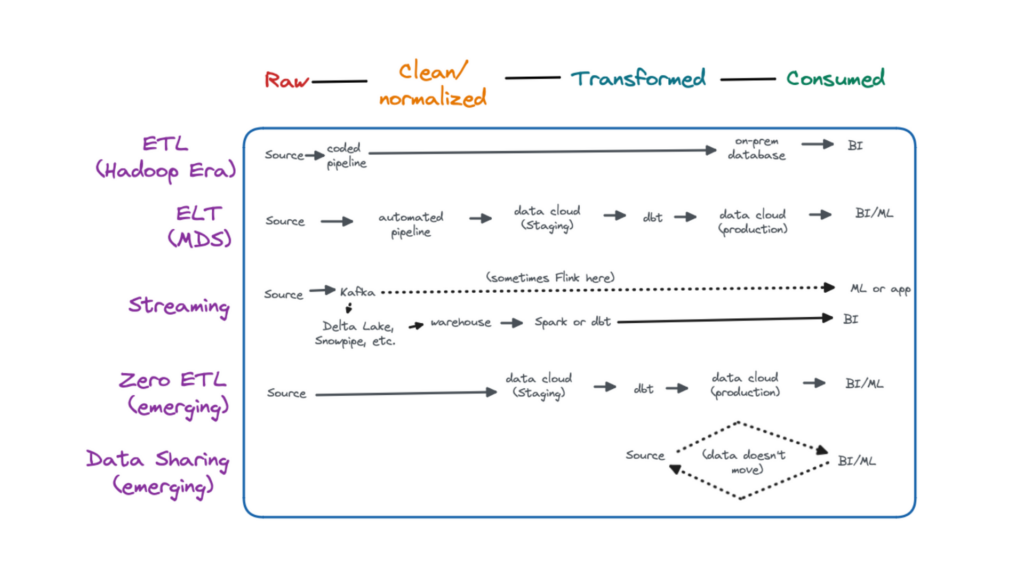
5 Data pipeline architecture designs and their evolution
ETL
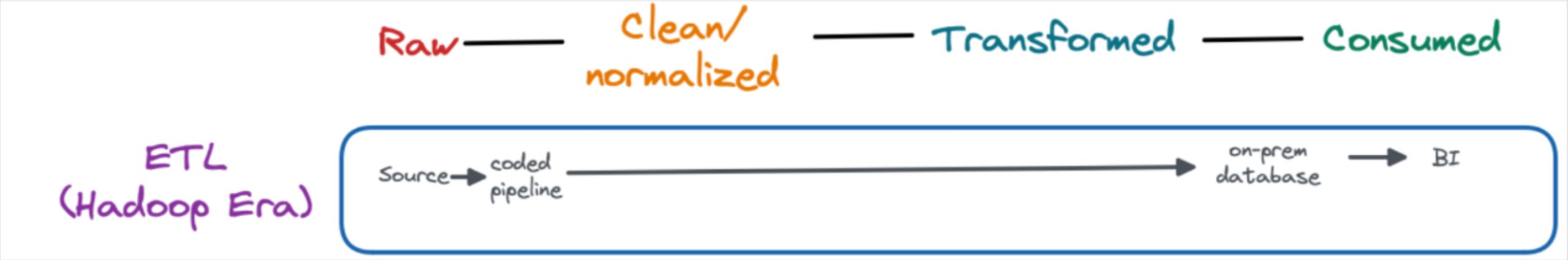
The Hadoop era, roughly 2011 to 2017, arguably ushered in big data processing capabilities to mainstream organizations.
Data then, and even today for some organizations, was primarily hosted in on-premises databases with non-scalable storage. Despite Hadoop’s parallel and distributed processing, compute was a limited resource as well.
As a result, data engineers spent considerable time modeling data and optimizing queries to fit within these constraints. Data pipeline architecture typically consisted of hardcoded pipelines that cleaned, normalized, and transformed the data prior to loading into a database using an ETL pattern.
Some organizations choose to still leverage an ETL pattern in the cloud, particularly for production pipelines where data contracts can help reduce data downtime.
ELT
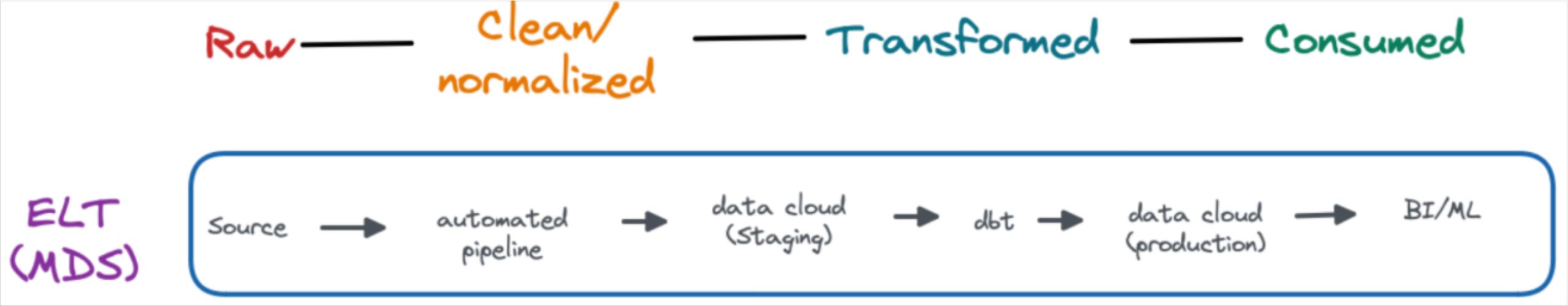
The modern data stack era, roughly 2017 to present data, saw the widespread adoption of cloud computing and modern data repositories that decoupled storage from compute such as data warehouses, data lakes, and data lakehouses. The term modern data stack refers to the multiple modular SaaS solutions that comprise the data platform and pipeline (more on those later).
With cost and physical compute/storage limitations largely lifted, data engineers started to optimize data pipeline architecture for speed and agility. Data could now be extracted and loaded prior to being transformed for its ultimate use. This scale and flexibility of the cloud and an ELT design pattern unlocked additional valuable use cases such as more widespread analytics, experimentation, and machine learning applications.
Streaming
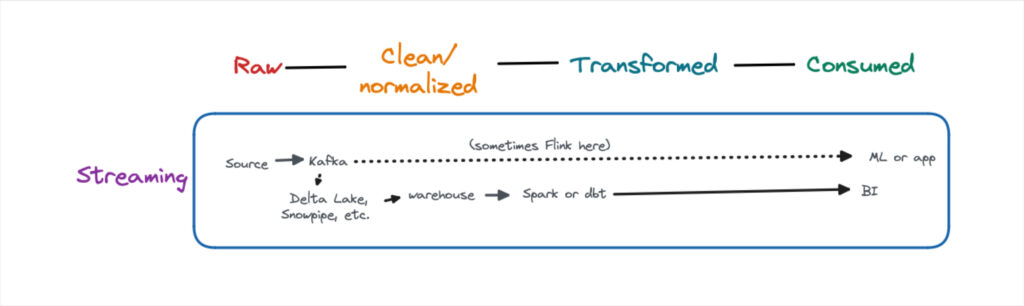
While these batch data pipelines were ideal for analytical use cases, there has been an increased need for near-real time data. Streaming data pipeline architectures are typically run in parallel to modern data stack pipelines and used mainly for data science or machine learning use cases. Apache Kafka is the most common tool and it comes in many flavors (Confluent Cloud, AWS MSK, self-hosted, etc).
The pattern can be described as stream, collect, process, store, and analyze. The most common architecture involves sending raw data directly to the application, but sometimes Flink is used as part of the transformation process. Another common pattern is to also land this data in a lake/lakehouse, eventually making its way to a warehouse for analytical use cases.
The direct source to application streaming data pipeline architecture can present challenges such as the inability to fully validate data quality or model the data. However, the value and benefits of near-real time data are hard to deny.
Data pipeline architectures are constantly being reinvented. Two emerging data pipeline architectures include zero ETL and data sharing.
Zero ETL
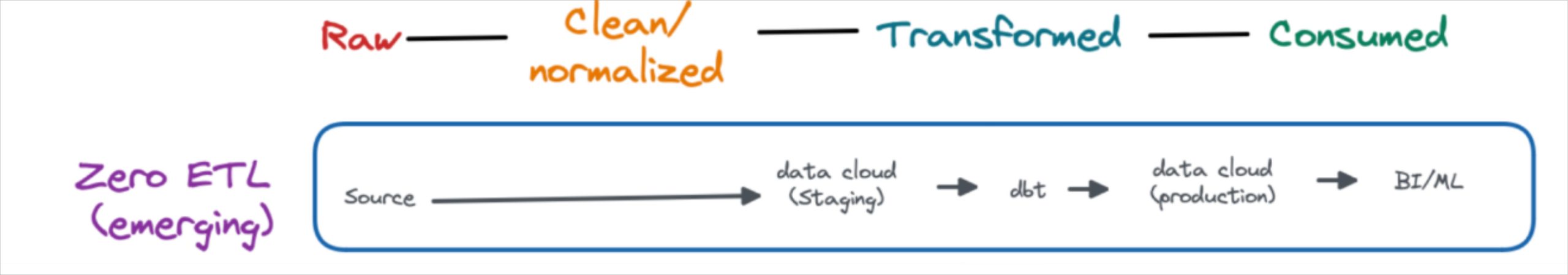
Zero ETL is a bit of a misnomer. These pipelines differ from traditional ELT pipelines by doing the data cleaning and normalization prior to load. In many cases the data stays in a data lake and is queried from there versus moving to the data warehouse.
At the moment, this tight integration is possible because most zero-ETL architectures require both the transactional database and data warehouse to be from the same cloud provider. Some examples include AWS (Aurora to Redshift), GCP (BigTable to BigQuery) and Snowflake (Unistore).
This trend is competing with another data pipeline architecture undercurrent where some organizations are considering decoupling their storage and compute at the vendor level with companies like Tabular.
Data Sharing
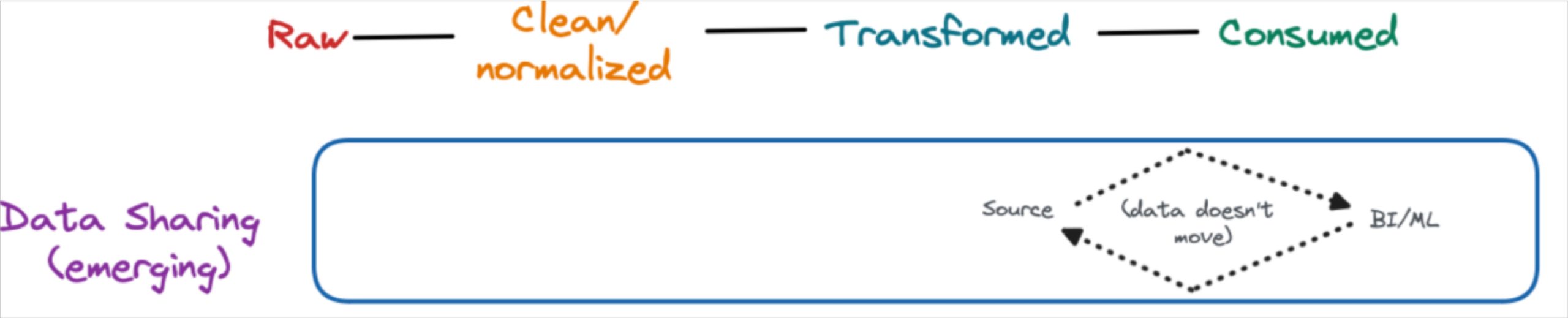
No copy data sharing is another emerging data pipeline architecture being pioneered by Snowflake (Secure Data Sharing) and Databricks (Delta Sharing). Unlike ZeroETL, this process actually doesn’t involve ETL and instead provides expanded access (permissions) to the data where it’s stored.
Remember, these aren’t a binary choice. Most organizations deploy some or all of these data pipeline architectures.
Common data pipeline solutions within the modern data stack
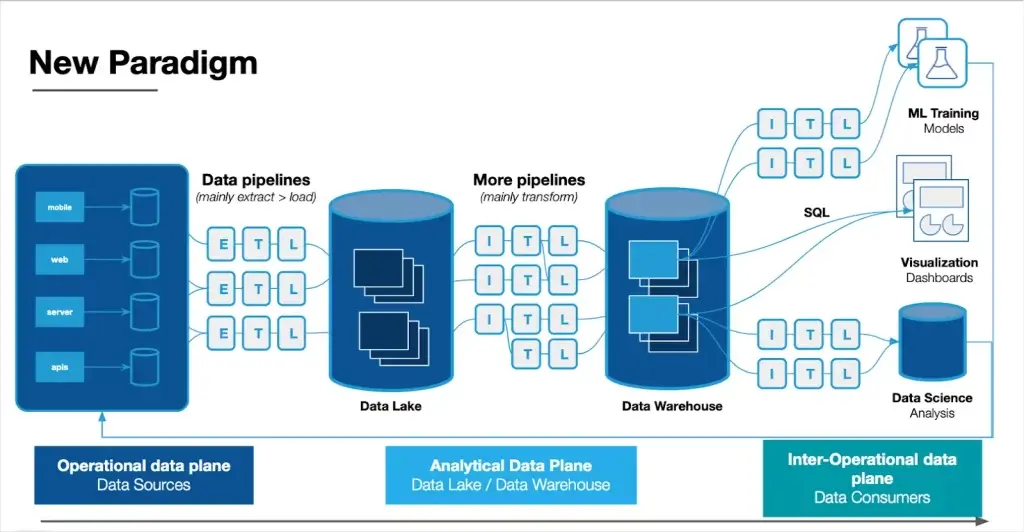
The modern data stack universe has a data warehouse, lake, or lakehouse as its center of gravity with numerous, modular solutions that integrate with one another orbiting around it.
If you zoom out to look across the entire data platform solution landscape it can get confusing and messy really quickly (although LakeFS does do a nice job organizing it in the image below).
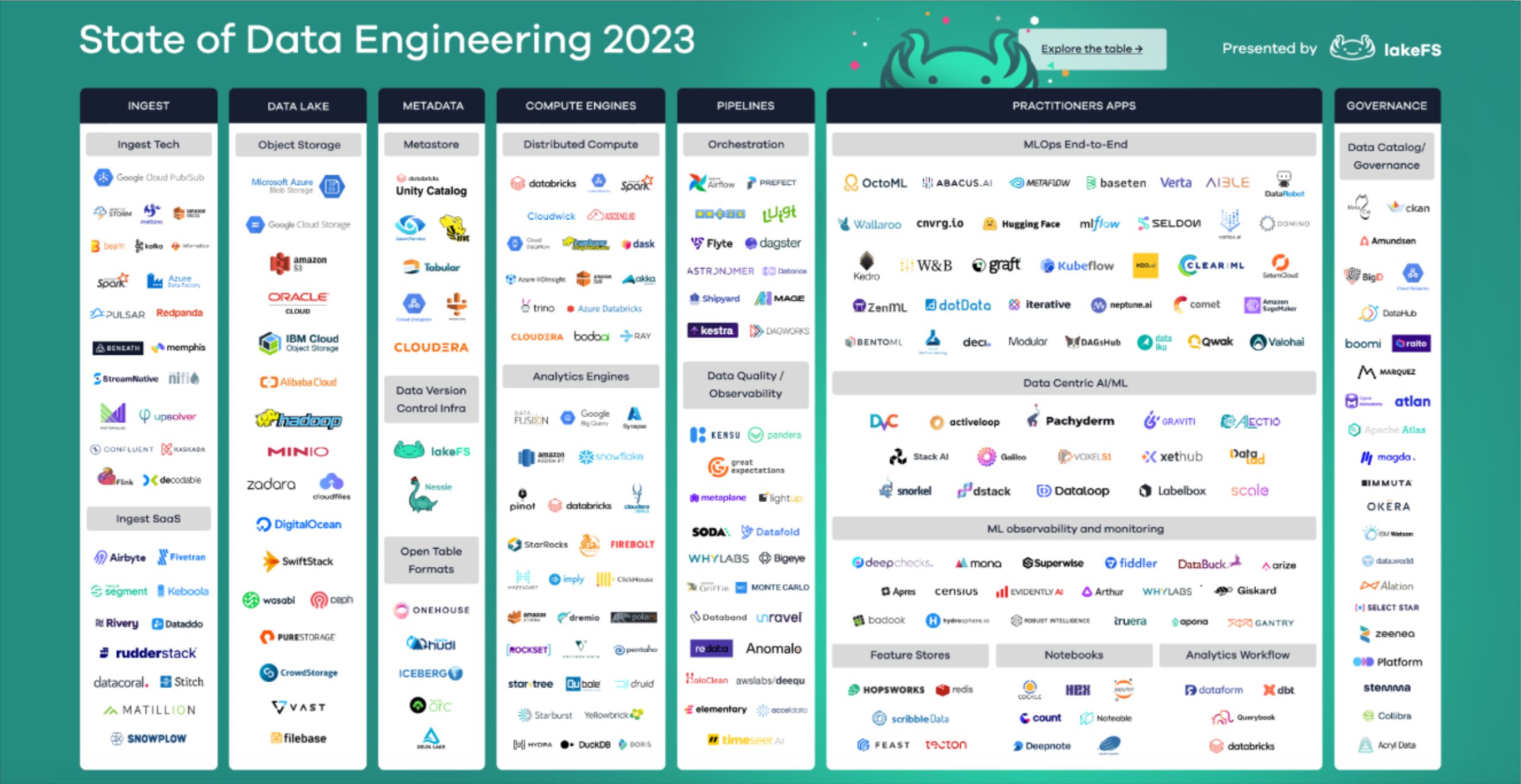
That’s why it can be more helpful to consider these solutions by the role they play within modern data pipeline architecture. This is frequently referred to as a 5 or 7 layer (depending on who you ask) data stack like in the image below.
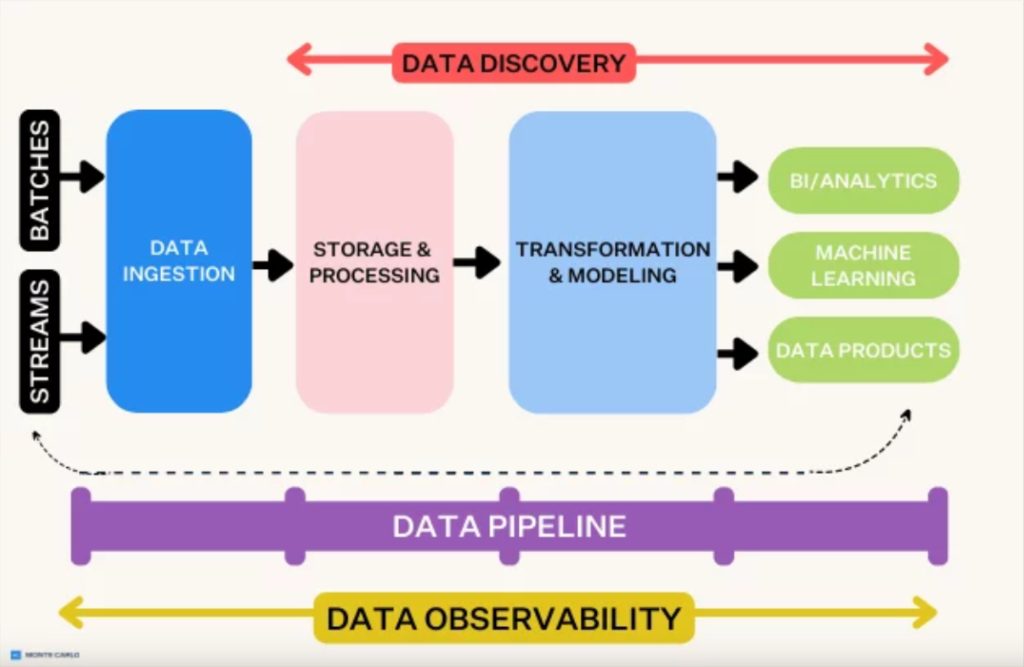
Here are some of the most common solutions that are involved in modern data pipelines and the role they play.
Data storage and processing
Don’t forget the SQL query code (or whatever language you are using with Spark) is part of your data pipeline architecture! Data flows from table to table (or dataframe) within your data repository and query changes can dramatically impact quality and performance.
- Snowflake – The original cloud data warehouse, Snowflake provides a flexible payment structure for data teams, as users pay separate fees for computing and storing data.
- Google BigQuery – Google’s cloud warehouse, BigQuery, provides a serverless architecture that allows for quick querying due to parallel processing, as well as separate storage and compare for scalable processing and memory.
- Amazon Redshift – Amazon Redshift, one of the most widely used options, sits on top of Amazon Web Services (AWS) and easily integrates with other data tools in the space.
- Firebolt – A SQL-based cloud data warehouse that claims its performance is up to 182 times faster than other options, as the warehouse handles data in a lighter way thanks to new techniques for compression and data parsing.
- Microsoft Azure – Microsoft’s cloud computing entrant in this list common among teams that leverage heavy Windows integrations.
- Amazon S3 – An object storage service for structured and unstructured data, S3 gives you the compute resources to build a data lake from scratch.
- Databricks – Databricks, the Apache Spark-as-a-service platform, has pioneered the data lakehouse, giving users the options to leverage both structured and unstructured data and offers the low-cost storage features of a data lake.
- Dremio – Dremio’s data lake engine provides analysts, data scientists, and data engineers with an integrated, self-service interface for data lakes.
Data ingestion
Batch data ingestion solutions include:
- Fivetran – A leading enterprise ETL solution that manages data delivery from the data source to the destination.
- Singer – An open source tool for moving data from a source to a destination.
- Stitch – A cloud-based open source platform that allows you to rapidly move data from a source to a destination.
- Airbyte – An open source platform that easily allows you to sync data from applications.
Data streaming ingestion solutions include:
- Apache Kafka – Confluent is the vendor that supports Kafka, the open source event streaming platform to handle streaming analytics and data ingestion. They also recently acquired Apache Flink, another streaming solution.
- Amazon Kinesis– A streaming solution from AWS that may be ideal for those utilizing Redshift as their data warehouse.
- Google Pub/Sub– A GCP service that enables you to ingest streaming data into BigQuery, data lakes, or operational data bases. Google made waves last year when they announced the ability to stream Pub/Sub directly into BigQuery without pipelines.
- Apache Spark– Labeled as a unified analytics engine for large scale data processing, many leverage this open source solution for streaming use cases, often in conjunction with Databricks.
Data orchestration
- Airflow: Airflow is the most common data orchestrator used by data teams. It is like a smart scheduler for your data workflows. It helps you schedule, monitor, and manage the flow of data between different tasks or steps, making sure everything happens in the right order and at the right time.
- Other common orchestration solutions include Prefect, Dagster, and Mage.
Data transformation
- dbt – Short for data build tool, is the open source leader for transforming data once it’s loaded into your warehouse.
- Dataform – Now part of the Google Cloud, Dataform allows you to transform raw data from your warehouse into something usable by BI and analytics tools.
- Sequel Server Integration Services (SSIS) – Hosted by Microsoft, SSIS allows your business to extract and then transform that data from a wide variety of sources which you can then later use to load into your destination of choice.
- Custom Python code and Apache Airflow – Before the rise of tools like dbt and Dataform, data engineers commonly wrote their transformations in pure Python. While it might be tempting to continue using custom code to transform your data, it does increase the chances of errors being made as the code is not easily replicable and must be rewritten every time a process takes place.
Business intelligence and analytics
- Looker – A BI platform that is optimized for big data and allows members of your team to easily collaborate on building reports and dashboards.
- Sigma Computing – A BI platform that delivers cloud-scale analytics with the simplicity of a spreadsheet and familiar data visualizations.
- Tableau – Often referred to as a leader in the BI industry, it has an easy-to-use interface.
- Mode – A collaborative data science platform that incorporates SQL, R, Python, and visual analytics in one single UI.
- Power BI – A Microsoft-based tool that easily integrates with Excel and provides self-service analytics for everyone on your team.
Data observability
- Monte Carlo– The creator and leader of the data observability category. Data observability platforms reduce your data downtime up to 80% and make your data engineers 30% more time efficient by replacing static, cumbersome data testing with machine learning models that can help detect, resolve, and prevent data issues.
Data catalog
Some organizations choose to implement data catalog solutions for data governance and compliance use cases. Data catalogs leverage the metadata generated through a modern data platform to provide descriptive information on critical data assets such as tables, key metrics, and more. Think of an automatically updating encyclopedia for your data platform.
We have compiled a list of the best data catalog tools.
Access management
You want the data in your modern data platform to be highly available only to those who have a need to access it. Access management solutions have become more critical as a means to protect sensitive information and PII as well as to avoid fines from data regulations such as GDPR or CCPA. Vendors in this space include:
- Immuta– Removes the complexity of managing and enforcing data policies so that organizations can speed up access to data without compromising security.
- BigID– A modern, extensible platform for privacy, protection, and perspective – across all data, everywhere.
- Privacera– Automates data access, security and policy management across multiple cloud services from a single, unified interface.
- Okera– Provides multiple enforcement patterns and platform-agnostic, policy-based data access control so policies are enforced consistently across all environments.
- SatoriCyber– Decouples security, privacy and access controls from the data layer, enabling data teams to move faster.
And all of this doesn’t include solutions common to data science pipeline architecture such as notebooks, feature stores, metastores MLOps and more.
7 Data Pipeline Architecture Best Practices
- Map and understand the dependencies of your data pipeline using an automated data lineage solution. No human can keep track of all the different dependencies within a complex data pipeline and documentation (when it exists) rarely gets the job done. Without this context your data team will either unintentionally commit breaking changes or petrified to change anything for fear of causing havoc downstream. Check out our article on 17 data lineage use cases for more context.
- Design your data pipeline so it is modular and automated. Your team will need to make frequent changes so a simple, modular pipeline that is easy to change is often better than the perfect pipeline that needs to be completely refactored each time data changes at the source. While open source data pipeline solutions are attractive from a cost perspective, keep in mind the cost of maintenance. Integrations are typically lagging and teams can spend more time on their architecture than getting value from it.
- Create data pipeline SLAs (service level agreements). It’s crucial to match the data pipeline architecture to the use case. Do your consumers need data refreshed every second, minute, hour or day? That will likely determine if your data pipeline architecture will feature stream, micro-batch, or batch ingestion. Does data quality need to be high will directionally accurate suffice? Codifying these expectations keeps all parties accountable.
- Let the data drive the data pipeline architecture. Most data teams will be handling mostly structured data for analytical purposes making a data warehouse based data pipeline architecture a natural fit. Some data teams may be handling more unstructured data for data science use cases and consider a data lake. Others may have to create more custom built architectures as Netflix Studios Senior Data Engineer Dao Mi told us about his time at Nauto, which develops AI software for driver safety. “There the main data types we handled were telemetry and video from the dashcams. Our storage and infrastructure paradigm was built around how we could best process this data, which essentially meant a lot of homegrown builds because commercial options didn’t exist,” he said.
- Create data products. Data-as-a-product is a shift in thinking introduced in Zhamak Dehgani’s data mesh concept. A data product is a data asset (typically important tables or dashboards) that holds significant value for the company. Data products are discoverable, secure, governed, trustworthy (high data quality), and interoperable.
- Continuously review and optimize costs. Poorly written and degrading queries are not only expensive, but they can create data reliability issues as well. Check out some helpful strategies for optimizing Snowflake costs and identifying these problematic queries.
- Make pipelines idempotent. If you don’t make your pipelines idempotent, meaning that executing an operation multiple times produces the same result as executing it once, you can prevent inconsistent or duplicate data.
6 Data Pipeline Architecture Diagrams From Real Data Teams
JetBlue‘s data pipeline architecture
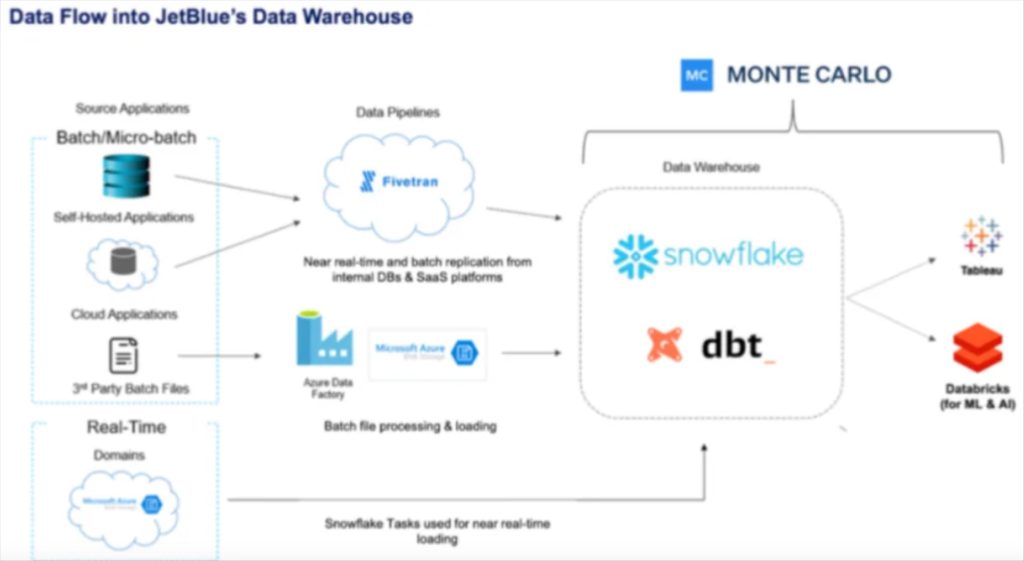
JetBlue’s data pipeline architecture balances multiple data sources and data freshness requirements. Snowflake Tasks are used for near real-time loading in lieu of a more traditional streaming data pipeline architecture. FiveTran is used to batch ingest data which lands in Snowflake and is transformed by dbt and monitored for quality by Monte Carlo. Databricks supports it’s ML and AI use cases. Learn more by checking out the webinar they did with Snowflake.
Fox Networks‘ data pipeline architecture
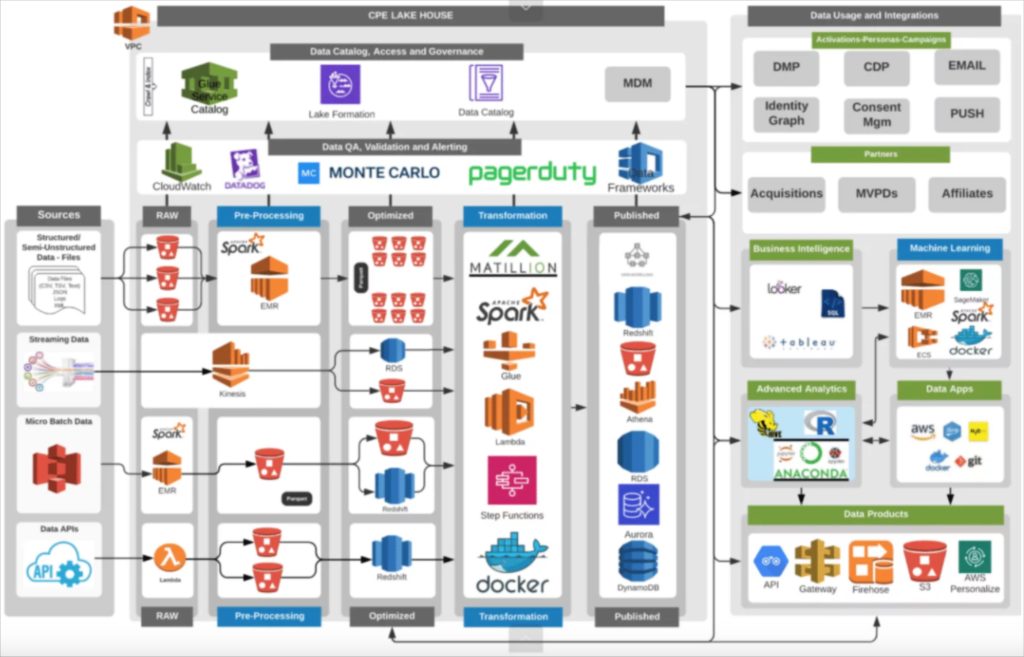
Fox’s data pipeline architecture is designed for resilience and reliability, in alignment with the network’s goals. When you are airing the Superbowl, you want everything to run without a hiccup. As such, reliability tools such as Datadog (application performance management), Monte Carlo (data observability), and PagerDuty (incident management) are all present. You can also see a robust streaming and microbatch architecture with Spark and various AWS services given their need for real-time data.
Fox’s VP of Data Services, Alex Tverdohleb told us his data pipeline architecture is designed with self-service in mind.
“Everything else, especially within data discovery and your ad-hoc analytics, should be free,” said Alex. “We give you the source of the data and guarantee it’s trustworthy. We know that we’re watching those pipelines multiple times every day, and we know that the data inside can be used for X, Y, and Z — so just go ahead and use it how you want. I believe this is the way forward: “striving towards giving people trust in the data platforms while supplying them with the tools and skill sets they need to be self-sufficient.”
Read more about Fox’s architecture.
Swimply‘s data pipeline architecture
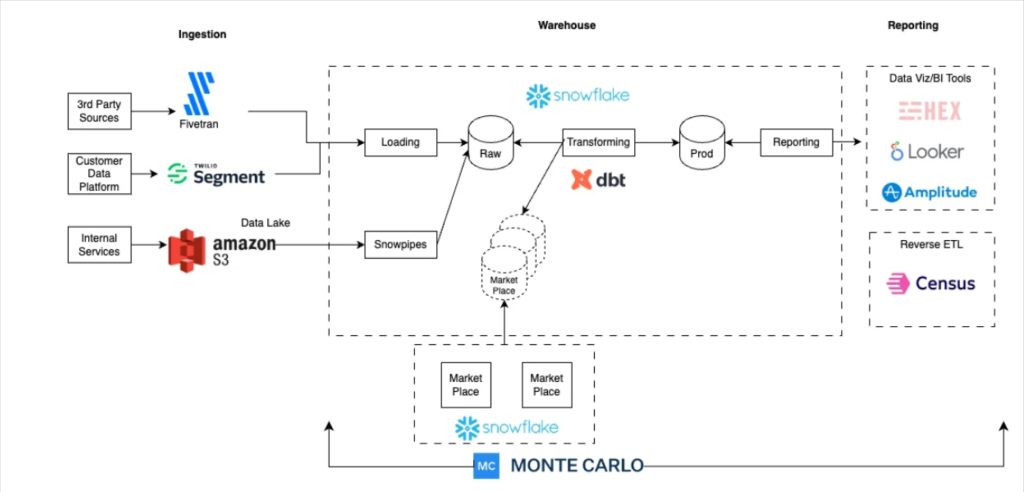
Startup Swimply’s data pipeline architecture is well-automated and designed with simplicity and scale in mind. Fivetran, Snowflake, dbt, Monte Carlo, and Looker are solutions that integrate very well together.
Head of data Michael Shledon says, “Because we had this mandate as a data team to support the entire company, we needed a data stack that could solve two central issues. One, to centralize all of the data from all of the different parts of the company in one stable place that everyone could use and refer to as a source of truth. And two, to enable us to have enough time to really focus on the insights and not just the data infrastructure itself.”
Read more about Swimly’s hypergrowth stack.
Backcountry‘s data pipeline architecture
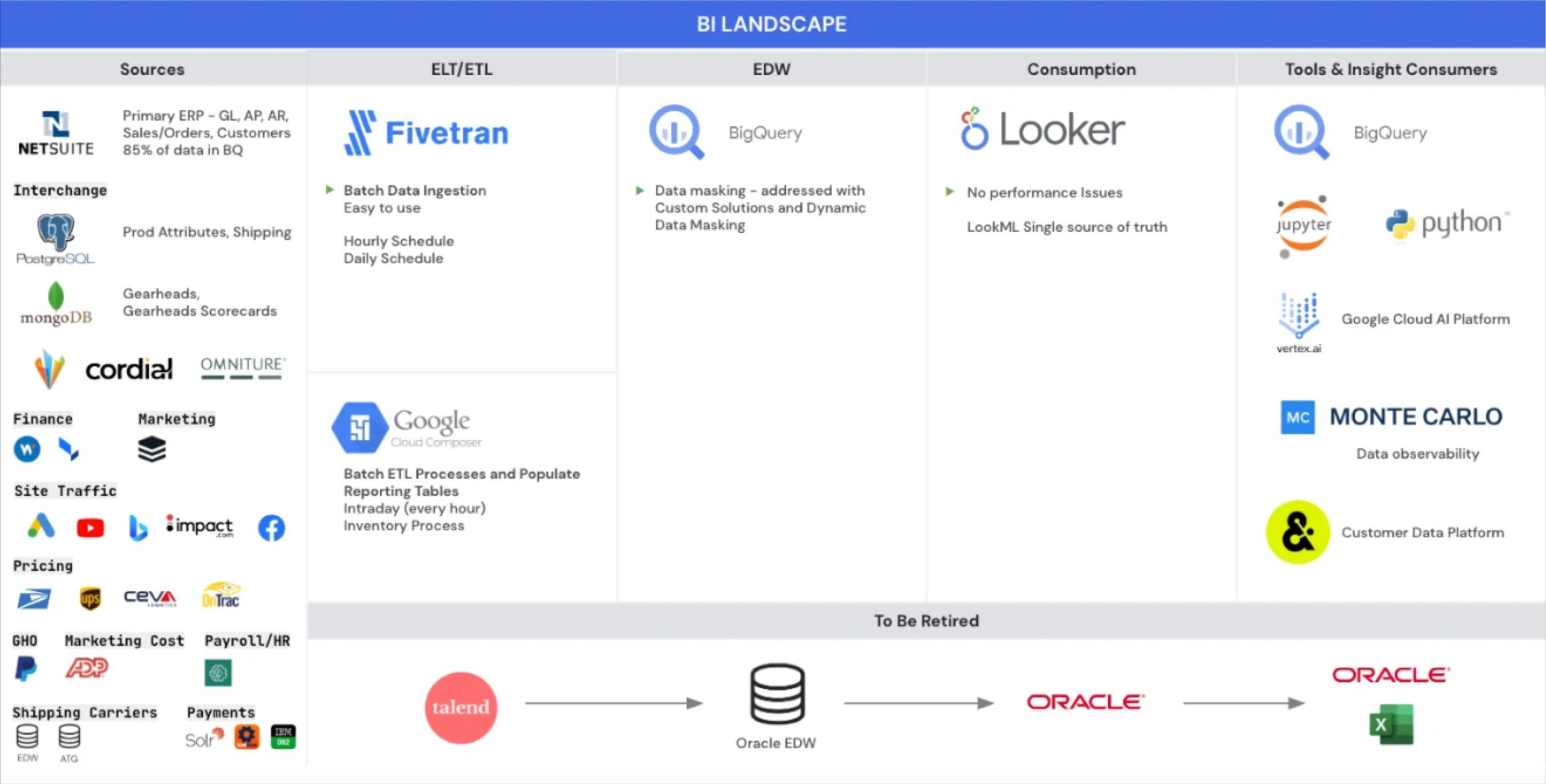
Backcountry relies on data to power nearly every facet of its business, including customer acquisition, segmentation and personalization, marketing, merchandising, and customer support. But the data team was ingesting large amounts of data from an ever-increasing number of sources, and the legacy system wasn’t able to perform at scale.
So the Backcountry team had to move quickly to migrate from a legacy stack to a modern data stack. They built their stack around the Google Cloud Platform, including BigQuery, Looker, Airflow, and Fivetran.
BlaBlaCar‘s data pipeline architecture
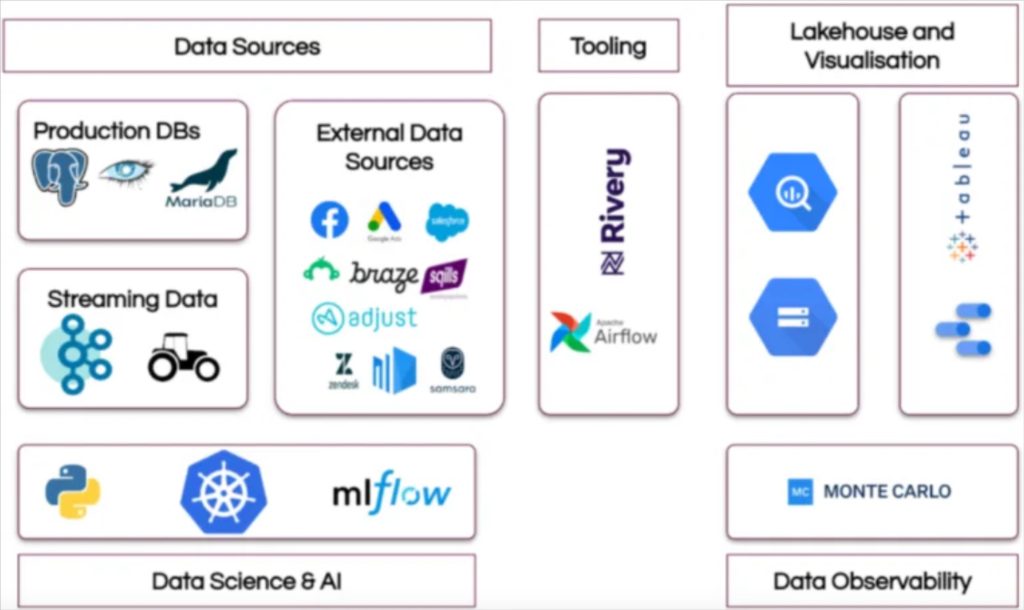
BlaBlaCar’s data pipeline architecture is part of its data mesh implementation. This transition to a more decentralized structure was critical to accelerate team efficiency following two M&As.
“We had some new use cases around data science that were hard to fit into our existing org. That’s essentially what triggered the discussion of ‘We need to do things differently,’” said Emmanuel Martin-Chave, VP of data analytics. Read more.
Drata‘s data pipeline architecture
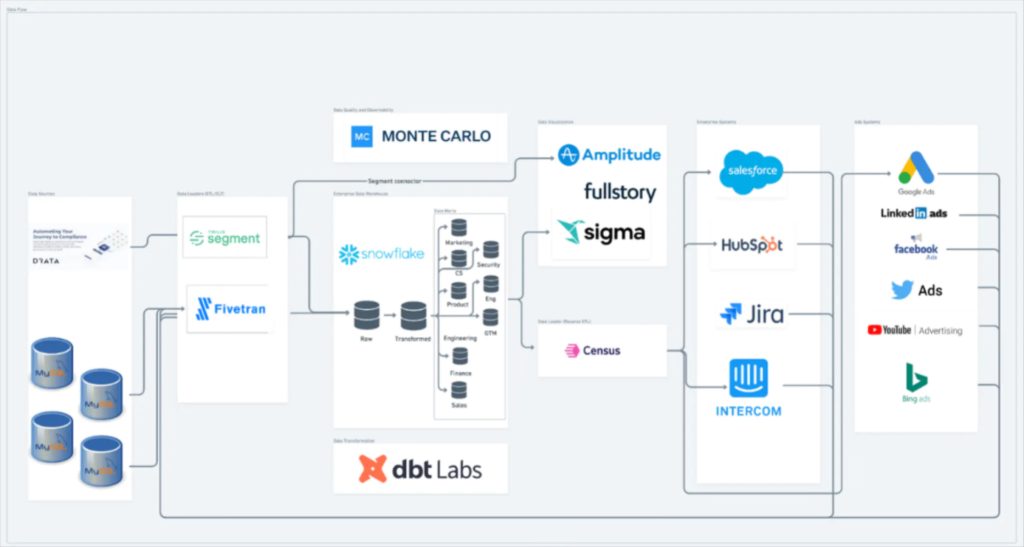
VP of data Lior Soloman got to build this modern data architecture from the ground up and he stood it up fast. He said, “Choosing the right technology stack is critical for a fast-growing startup. I wanted to select technologies that would scale with our fast-growing business, be easy to use, and seamlessly integrate with our existing systems.”
Now Go Build Some Data Pipelines!
Remember, it’s not about having the right data pipeline architecture, it’s about having the right data architecture for you.
Interested in adding data observability to your data pipeline architecture? Schedule a time to talk to us using the form below!
Our promise: we will show you the product.
 Product demo.
Product demo.  What is data observability?
What is data observability? 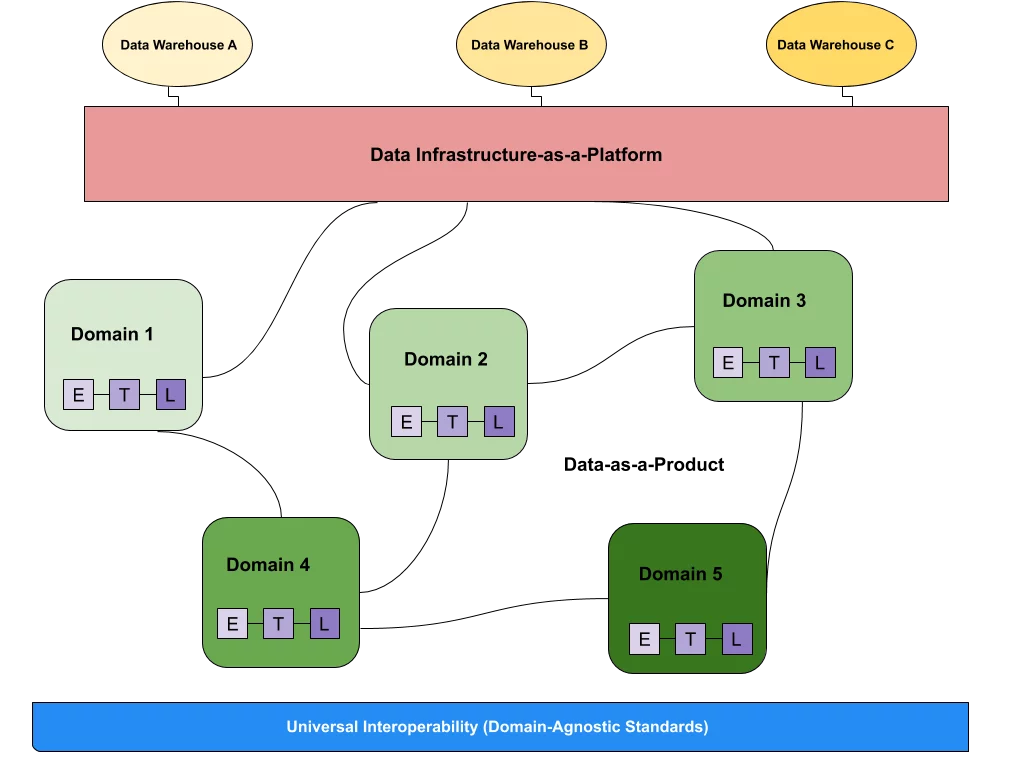 What is a data mesh--and how not to mesh it up
What is a data mesh--and how not to mesh it up  The ULTIMATE Guide To Data Lineage
The ULTIMATE Guide To Data Lineage