The Future of Data Warehousing

As every company becomes a data company, and more users within these companies are discovering new uses for previously unavailable data, existing infrastructure and tools are not just meeting that demand but creating new demands. At the center of it all is the data warehouse, the lynchpin of any modern data stack.
In this blog post, we’ll look at six innovations that are shaping the future of the data warehousing, as well as challenges and considerations that organizations should keep in mind.
Table of Contents
1. Data lake and data warehouse convergence
The data lake vs data warehouse question is constantly evolving.
The maxim that data warehouses hold structured data while data lakes hold unstructured data is quickly breaking down. Both have expanded their capabilities to support what the other does. Data warehouses like Snowflake or Google BigQuery have made improvements integrating streaming data capabilities while Databricks has added ACID properties via delta tables and its new Unity Catalog.
The result will be a convergence toward what’s called a “data lakehouse,” a best-of-both-worlds approach that will allow many more organizations to benefit from the business intelligence to be found within their data footprint.
2. Easier to stream real-time data
As data needs have changed, standards for data freshness and latency have come closer to real time. In industries like finance, ecommerce, and manufacturing, we’re going to see the rise of solutions that reduce the complexity of writing code to build real-time streaming pipelines.
Solutions like Confluent with Databricks allow organizations to prep, join, enrich and query streaming data sets in Databricks SQL, which they claim has up to 12x better price-performance than a traditional data warehouse. Similarly, Snowflake’s new Dynamic Tables and Snowpipe Streaming simplifies the traditionally complex process of managing batch and streaming data.
3. Zero-copy data sharing
Snowflake zero-copy cloning hints at the future of data warehousing.
Snowflake’s zero-copy cloning feature will see wider adoption, as evidenced by Snowflake’s recently expanded partnership with Salesforce allowing zero-copy cloning between the two.
Reducing the risks, costs, and headaches from traditional sharing methods, the feature allows organizations to share read-only database objects with other organizations without transferring the actual data.
A huge benefit is the separation of storage and compute. When an object is shared with a data consumer, it remains within the provider’s account, and the consumer incurs compute costs for querying the data, but no storage costs.
Not to be outdone, Databricks introduced its own zero copy data sharing capability with Delta Sharing, described as, “the world’s first open protocol for secure data sharing, making it simple to share data with other organizations regardless of which computing platforms they use.”
4. Zero ETL?
Beyond zero-copy data sharing, Amazon (AWS) has a grander vision for a zero ETL future altogether. In 2022 they first announced Amazon Aurora support for zero-ETL integration with Amazon Redshift, giving users the ability to move data between the two platforms without having to extract, transform and load first. A year later, they had four AWS database zero-ETL integrations with Amazon Redshift.
While zero ETL promises to free us up to focus on tasks like data analysis and interpretation rather than data preparation, it’s unclear whether it ends up just a gimmick with limited use.
For example, how easy will it be to perform complex data transformations? How will data governance be handled? And how hard will it be to interact outside of the zero ETL ecosystem?
We’ll have to see what the future holds.
5. Integration of ML models and AI capabilities
Data warehouses are becoming directly involved in not just storing data but also in processing and deriving insights through AI and ML models.
For example, Snowflake’s Cortex and Databricks’ LakehouseAI demonstrate this trend of integration and innovation. Cortex enables organizations to quickly analyze data and build AI applications — all within Snowflake. With just a single line of SQL or Python, analysts can instantly access specialized ML and LLM models tuned for specific tasks.
On the other hand, Databricks’ LakehouseAI represents a broader integration of AI and ML into their Lakehouse architecture. It offers features like vector search and feature serving, which significantly improve the handling of unstructured data, and the MLFlow Gateway, which facilitates the deployment and management of AI models.
6. Data issues identified and resolved faster
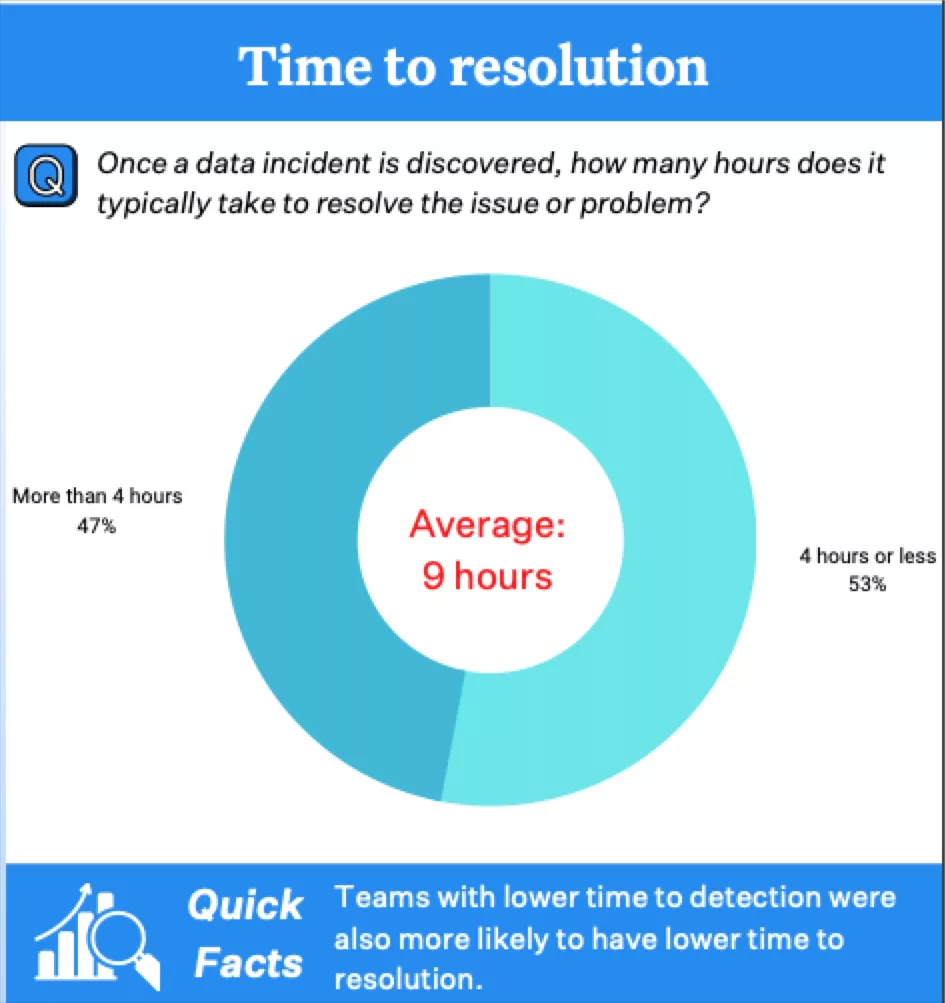
No matter what the future of data warehousing holds, if your users can’t rely on the underlying data itself, all of these innovations are for nothing.
Enter data observability platforms, which enable data teams to deliver more reliable and trustworthy data by operationally monitoring the health of data as it flows through the stack. These solutions dramatically reduce data downtime up to 80% or more by reducing the number of data issues, time to detection, and time to resolution.
The most successful data-driven companies already take advantage of these solutions, and data observability will only become more critical as every company becomes a data company.
A bright and rapidly evolving future
Data warehouses are at an exciting point of expansion and evolution. With the global data warehousing market size estimated to grow at a CAGR of 10% until 2028, you’ll see a greater reliance on them and the tools that make them easier to use than ever before.
Curious about the future of data warehousing? Interested in scaling data quality with data observability? Schedule a time to speak with us and check out Monte Carlo using the form below.
Our promise: we will show you the product.
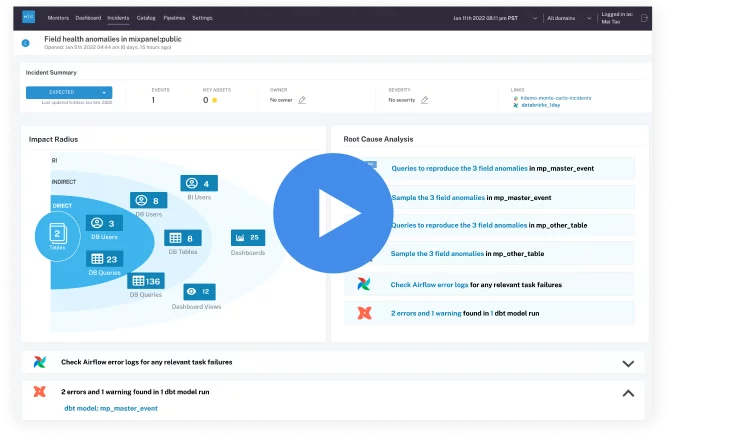 Product demo.
Product demo. 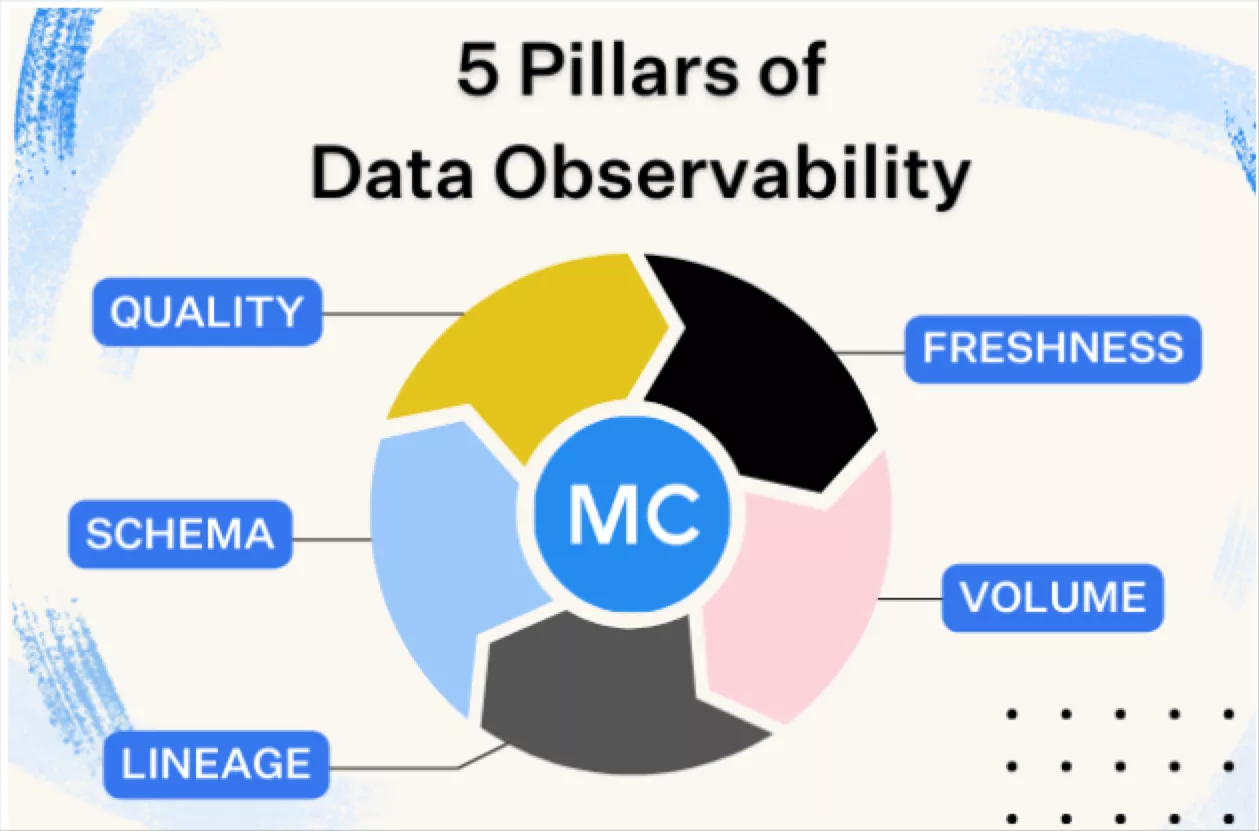 What is data observability?
What is data observability? 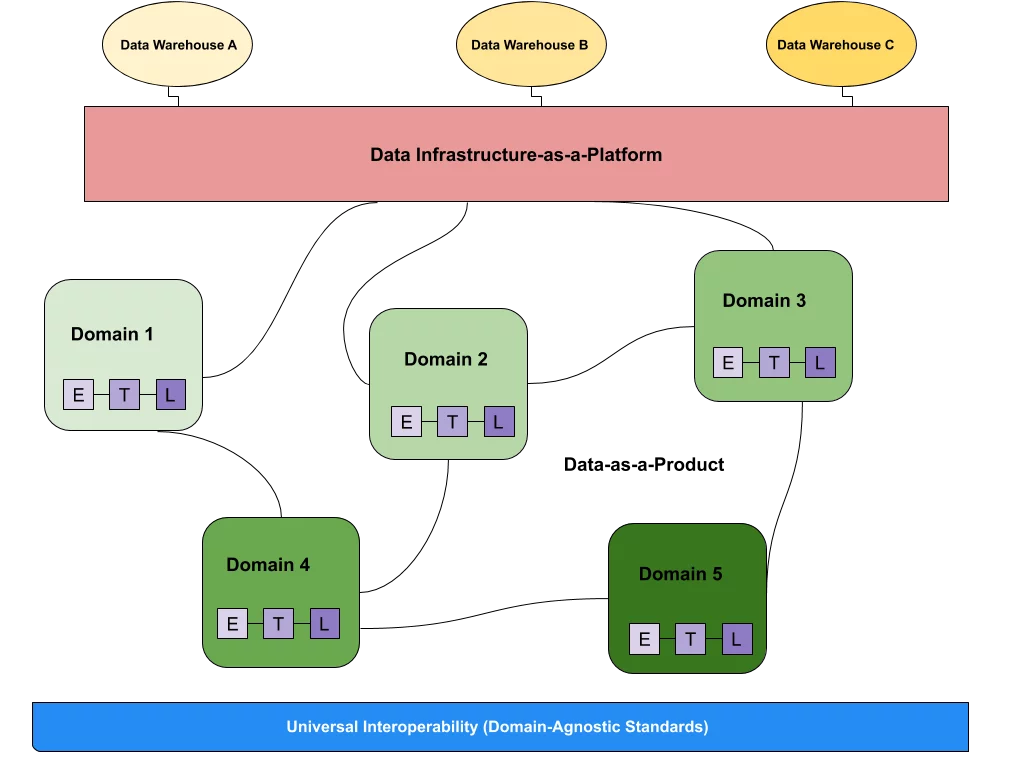 What is a data mesh--and how not to mesh it up
What is a data mesh--and how not to mesh it up  The ULTIMATE Guide To Data Lineage
The ULTIMATE Guide To Data Lineage