The Future of Data Governance: 4 Trends to Watch Out For

Data is among your company’s most valuable commodities, but only if you know how to manage it.
For most companies, data governance is now a “need-to-have” for several reasons:
- The rise of GDPR and other compliance measures that put data security under more intense scrutiny;
- The increased sophistication and technological prowess of bad actors seeking access to proprietary data;
- The proliferation of data usage across the company, as more and more teams require data access in their work; and
- Increasingly varied, complex, and distributed data architecture and data management.
More data, more access to data, and more regulations mean data governance has become a higher-stakes game. As you prepare to roll out a successful data governance strategy at your organization, keep an eye on the following four trends that will shape the future of data governance.
Data Governance Trends
The biggest data governance trend isn’t really a trend at all—rather, it’s a state of mind. Data governance is fast becoming an “all-company” problem, no longer relegated to disparate silos of the business. At the same time, data governance technologies are growing more intelligent.
The result is a win-win for data teams, which increasingly have both the organizational buy-in and the tools they need to launch data governance strategies that effectively maintain the availability, usability, and security of data.
Today’s data engineering teams have multiple options when it comes to designing data governance strategies that best suit their respective businesses. Here are four data governance trends to watch.
1. Cloud-based data governance
In some ways, it would be a disservice to call cloud-based data governance a trend, but it’s undeniable that the rise of the cloud has had a marked impact on how we ensure data compliance and discovery.
Modern data warehouses, data lakes, and data lakehouses have empowered multiple constituencies across companies to access and use data without always needing to tap the data engineering team for help.
Organizations are fast finding that cloud-based data access requires an equally nimble approach to data governance. Too many organizations are still enforcing data governance with highly manual, inefficient tools and processes. As data input channels and tech stacks become more complex and prolific, this manual approach to data governance just isn’t scalable.
Plus, a growing number of companies are leveraging cloud-based, distributed data architectures like data mesh. Without a comprehensive and flexible data governance strategy, companies will not be able to manage their data effectively.
2. Data governance as a service
Data governance isn’t one standalone tool or workflow—it’s a complex combination of people, processes, and tools that unite to give an organization better control over its data. Thus, multiple tools and technologies can work in harmony in service of an overarching data governance strategy.
Keep an eye out for the rise of an emerging new trend to tackle this: data governance as a service: i.e., the proliferation of third-party providers offering data governance services to help organizations manage their data more effectively. As you launch your own data governance strategy, look partners that can help you:
- Classify and map your existing data, so you have a clear picture of your company’s complete data landscape
- Store your data with a cloud-based platform that syncs well with automated tools
- Conduct data observability, to ensure your data is accurate, reliable, and trustworthy
- Create a data governance model, complete with goals, mission statements, roles and responsibilities, and accountability structures
As data governance becomes front-of-mind for every company, leveraging a growing number of tools and services can help make instituting data governance strategies easier and more scalable.
3. Enhanced focus on data lineage in Generative AI
As GenAI moves towards broader adoption and becomes integrated into various industries and applications, the ability to trace data’s journey – from its origin through various transformations to its ultimate use in AI models – becomes paramount.
This enhanced focus on data lineage not only aids in preemptive error detection but also plays a crucial role in post-hoc analysis, particularly when AI models yield unexpected or erroneous results.
Expect a shift towards more sophisticated and proactive data governance frameworks, where understanding the flow and usage of data in GenAI models is not just beneficial but essential for operational success and regulatory compliance.
I predict we’ll see data engineering teams ditch manual data governance processes in favor of automated cloud-based data governance tools, which teams can activate in mere minutes, and which yield better, more reliable results.
4. Automation of data governance
Say goodbye to manual data governance processes. The sheer volume of data today’s organizations manage makes it practically impossible for data engineering teams to govern data assets manually.
Thankfully, advances in AI and machine learning are making it possible to automate certain data governance tasks, like data observability.
Data observability is an organization’s ability to fully understand the health of the data in their systems. Built on five pillars—data freshness, quality, volume, schema, and lineage—data observability eliminates data downtime by applying best practices learned from DevOps to data pipeline observability.
Data observability platforms like Monte Carlo allow organizations to use automated monitoring, alerting, and triaging to evaluate data quality and discoverability issues. This makes it easier for data governance teams to monitor data changes, identify broken pipelines, and fix any problems more quickly. Ultimately, more reliable data is a critical part of any data governance strategy, which seeks to ensure data is not just accessible and secure, but also usable by various constituents across an organization.
Looking forward
It’s an exciting time to be in the data business—and data governance is only enhancing that excitement. Solid data governance strategies make it easier for organizations to use, discover, and apply their data—and the resulting possibilities are exciting and unlimited.
Technologies like data observability platforms are paving the way forward for more effective, automated, and scalable data governance strategies.
Interested in learning more about how data observability and data governance go hand-in-hand? Reach out to get started.
Our promise: we will show you the product.
 Product demo.
Product demo. 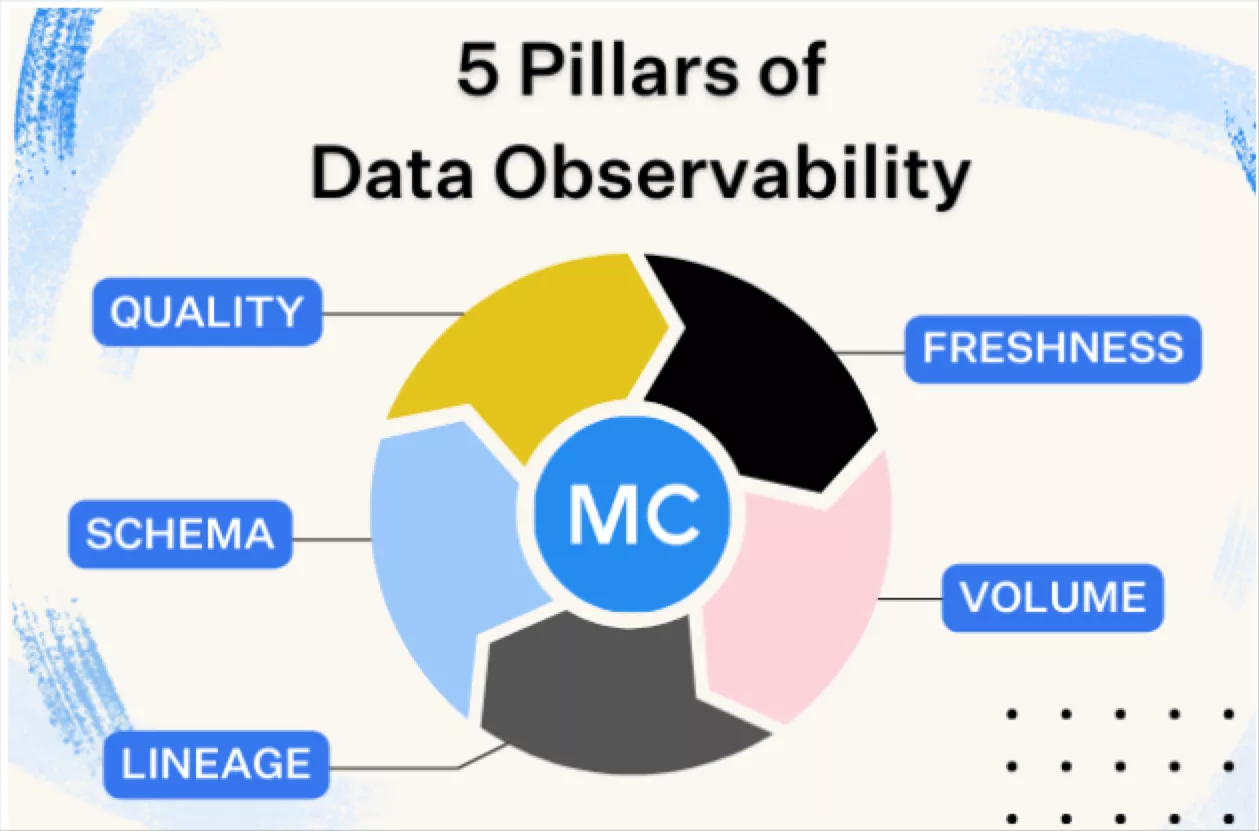 What is data observability?
What is data observability? 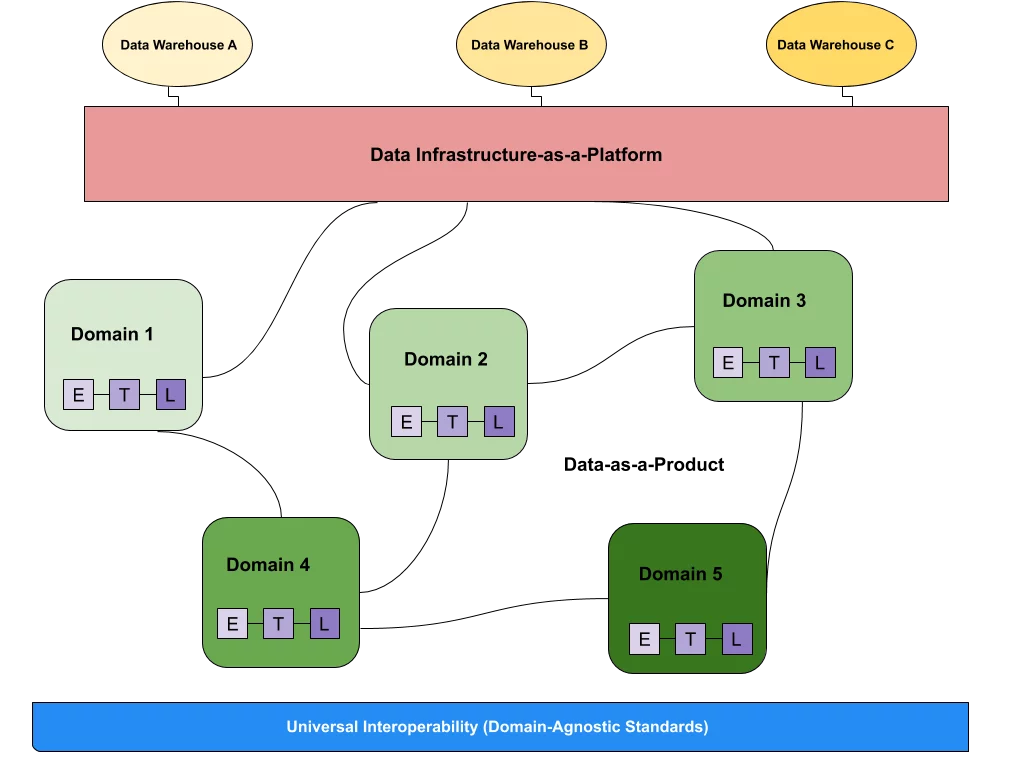 What is a data mesh--and how not to mesh it up
What is a data mesh--and how not to mesh it up 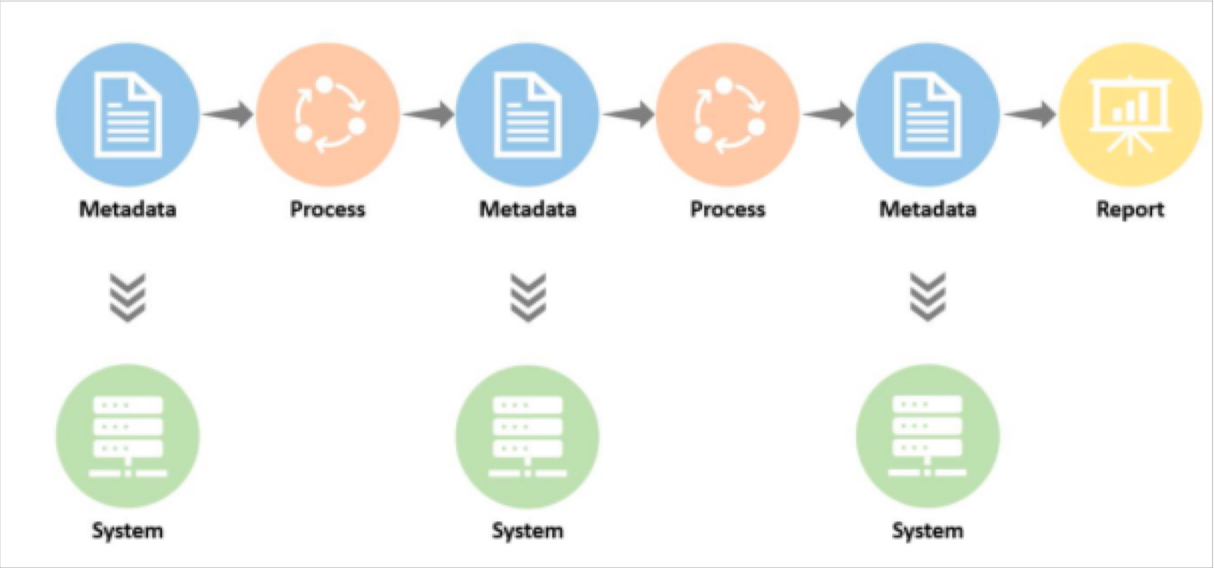 The ULTIMATE Guide To Data Lineage
The ULTIMATE Guide To Data Lineage